Difference between revisions of "Methodology"
Diego Failla (talk | contribs) |
Diego Failla (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[File:Flow chart.png|alt=|left|867x867px]] | [[File:Flow chart.png|alt=|left|867x867px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Phase 1 === | ||
| + | First, it was analyzed the current situation of QMS in 36 HEIs spread over 5 European countries (Portugal, Spain, Belgium, Lithuania and Italy), with particular emphasis being given to the quality indicators used in these systems. This work included desk research (analysis of different institutional documents, such as quality manuals, strategic plans and activities plans, as well as the institutions’ websites), combined with formal and informal contacts with the institutions included in the sample. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The sample was made of 21 universities, 4 polytechnic institutes, 2 universities of applied sciences, 7 schools and 2 colleges. While 27 are public HEIs, 9 are private ones. Regarding their size, the sample comprises rather small institutions, with less than 5,000 students (12 HEIs), medium sized ones, with a number of students ranging from 5,000 to 15,000 (12HEIs), as well as large institutions, with a number of students that goes well beyond the 20,000 students (12 HEIs). 12 of the institutions have only one campus, while 24 of them are located at multi campuses. Furthermore, most of the HEIs are comprehensive (24) with only 8 having a specific character. Finally, while 20 are located in metropolitan cities (Milan, Barcelona, Lisbon, Vilnius and Brussels), 16 are placed in regional cities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The reasons for the selection of these institutions/QMS are varied, ranging from the characteristics of the institutions themselves (e.g. history, dimension, representativeness and relevance within the national higher education systems, good positions in international rankings, reputation), to the easiness of contact with relevant people within the institution (augmenting the possibility of collecting reliable and valid information on the QMS), the availability of public information on the QMS, including when searching the institutional website (e.g. on the process and the role played by each body, in a transparent way), the existence of well-structured and integrated governance and management systems, interested in promoting the quality of the nuclear processes and their results, ensuring the involvement of all stakeholders, or the maturity level of the QMS. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, 223 quality indicators have been identified in the 36 QMS analyzed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Phase 2 === | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 25 November 2021
The aim of the SMART-QUAL project is not the creation of an exhaustive and extensive compilation of all possible Quality Indicators already in use or able for use, but of a SMART set that could be defined as follows:
a) Short: focused on the efficiency and effectiveness of IQAS and avoiding oversizing.
b) Meaningful: useful for the stakeholders’ needs, mainly from IQAS from HEIs, Quality Agencies, and the Higher Education community.
c) Appropriate: meeting the common and shared quality standards, which, in an European context, are specified in the ESG, supported by ENQA and other relevant stakeholders.
d) Reunified: harmonized set and compilated good practices already in use.
e) Transversal: suitable for different countries, contexts, and types of HEIs.
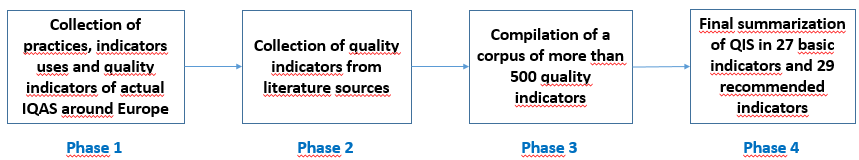
According to this aim, the QIS construction methodology has been divided into four main phases, as shown in the figure below.
Phase 1
First, it was analyzed the current situation of QMS in 36 HEIs spread over 5 European countries (Portugal, Spain, Belgium, Lithuania and Italy), with particular emphasis being given to the quality indicators used in these systems. This work included desk research (analysis of different institutional documents, such as quality manuals, strategic plans and activities plans, as well as the institutions’ websites), combined with formal and informal contacts with the institutions included in the sample.
The sample was made of 21 universities, 4 polytechnic institutes, 2 universities of applied sciences, 7 schools and 2 colleges. While 27 are public HEIs, 9 are private ones. Regarding their size, the sample comprises rather small institutions, with less than 5,000 students (12 HEIs), medium sized ones, with a number of students ranging from 5,000 to 15,000 (12HEIs), as well as large institutions, with a number of students that goes well beyond the 20,000 students (12 HEIs). 12 of the institutions have only one campus, while 24 of them are located at multi campuses. Furthermore, most of the HEIs are comprehensive (24) with only 8 having a specific character. Finally, while 20 are located in metropolitan cities (Milan, Barcelona, Lisbon, Vilnius and Brussels), 16 are placed in regional cities.
The reasons for the selection of these institutions/QMS are varied, ranging from the characteristics of the institutions themselves (e.g. history, dimension, representativeness and relevance within the national higher education systems, good positions in international rankings, reputation), to the easiness of contact with relevant people within the institution (augmenting the possibility of collecting reliable and valid information on the QMS), the availability of public information on the QMS, including when searching the institutional website (e.g. on the process and the role played by each body, in a transparent way), the existence of well-structured and integrated governance and management systems, interested in promoting the quality of the nuclear processes and their results, ensuring the involvement of all stakeholders, or the maturity level of the QMS.
Overall, 223 quality indicators have been identified in the 36 QMS analyzed.